Ascaris lumbricoides
| Ascaris lumbricoides | |
|---|---|
| |
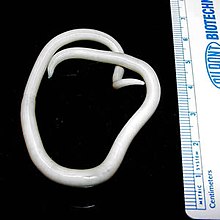
| An adult female Ascaris worm | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Chromadorea |
| Order: | Ascaridida |
| Family: | Ascarididae |
| Genus: | Ascaris |
| Species: | A. lumbricoides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ascaris lumbricoides | |
Ascaris lumbricoides is a large parasitic roundworm of the genus Ascaris. It is the most common parasitic worm in humans.[1] An estimated 807 million–1.2 billion people are infected with A. lumbricoides worldwide.[2] People living in tropical and subtropical countries are at greater risk of infection. Infection by Ascaris lumbricoides is known as ascariasis.[3]
It has been proposed that Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum (pig roundworm) are the same species.[4]
Life cycle
[edit]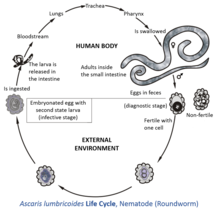
Ascaris lumbricoides, a roundworm, infects humans via the fecal-oral route. Eggs released by adult females are shed in feces. Unfertilized eggs are often observed in fecal samples but never become infective. Fertilized eggs embryonate and become infectious after 18 days to several weeks in soil, depending on the environmental conditions (optimum: moist, warm, shaded soil).[5]
Infection occurs when a human swallows water or food contaminated with embryonated eggs. In the duodenum, a single rhabditiform larva hatches from each of the ingested eggs. The larvae then penetrate the mucosa and submucosa and enter the venules or lymphatic vessels. From there, the larvae then pass through the heart to enter the pulmonary circulation. The larvae then break through the walls of the pulmonary capillaries to enter the alveoli.[6][7] The juvenile worms then migrate from the alveoli, through the bronchioles and bronchi, and into the trachea. An acute inflammatory reaction can occur if some of the worms get lost during this migration process and accumulate in other organs of the body.[7]
Once in the trachea, the worms are coughed up into the pharynx and then swallowed again, after which they pass through the stomach and into the small intestine, where they mature into adult worms.[5][7] The adult worms begin producing fertilized eggs within 60–65 days of being swallowed;[7] females produce as many as 200,000 eggs per day for 12–18 months. These fertilized eggs become infectious after two weeks in soil; they can persist in soil for 10 years or more.[6]
It might seem odd that the worms end up in the same place where they began. One hypothesis to account for this behavior is that the migration mimics an intermediate host, which would be required for juveniles of an ancestral form to develop to the third stage. Another possibility is that tissue migration enables faster growth and larger size, which increases reproductive capacity.[7] The eggs have a lipid layer which makes them resistant to the effects of acids and alkalis, as well as other chemicals.[8]
Morphology
[edit]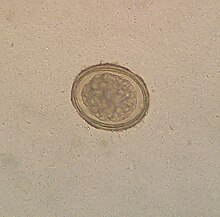


Ascaris lumbricoides is characterized by its great size. Males are 2–4 mm (0.08–0.2 in) in diameter and 15–31 cm (5.9–12 in) long. The male's posterior end is curved ventrally and has a bluntly pointed tail. Females are 3–6 mm (0.1–0.2 in) wide and 20–49 cm (7.9–19 in) long. The vulva is located in the anterior end and accounts for about one-third of its body length. Uteri may contain up to 27 million eggs at a time, with 200,000 being laid per day. Fertilized eggs are oval to round in shape and are 45–75 μm (0.0018–0.0030 in) long and 35–50 μm (0.0014–0.0020 in) wide with a thick outer shell. Unfertilized eggs measure 88–94 μm (0.0035–0.0037 in) long and 44 μm (0.0017 in) wide.[9]
Epidemiology
[edit]An estimated 807 million–1.2 billion people are infected with A. lumbricoides worldwide.[2] While infection occurs throughout most of the world, ascariasis is most common in sub-Saharan Africa, the Americas, China, and east Asia.[10] Although the prevalence is low in the United States, ascariasis is still endemic in the southeastern United States due to the temperature and humid climate.[11]
A. lumbricoides eggs are extremely resistant to strong chemicals, desiccation, and low temperatures. The eggs can remain viable in soil for months or even years.[9] Eggs of A. lumbricoides have been identified in coprolites in the Americas, Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and New Zealand, the oldest ones being more than 24,000 years old.[12]
Infections
[edit]Infections with these parasites are more common where sanitation is poor,[13] and raw human feces are used as fertilizer.[14]
Symptoms
[edit]Often, no symptoms are presented with a minor A. lumbricoides infection, the inevitable consequence being the e.g. once a year passage of such clearly visible worm(s) on close inspection. In the case of bad infections symptoms commonly include bloody sputum, cough, fever, abdominal discomfort, intestinal ulcer(s), as well as a less commonly missed passing of the quite long worms.[15][16] Ascariasis is the most common cause of Löffler's syndrome worldwide. Accompanying pathological symptoms include pulmonary infiltration, eosinophilia (symptoms of the overabundance of eosinophils in the blood such as asthma and allergic reactions), and a diagnostic symptom is, aside from standard microscopy of stools, radiographic opacities.[17] One study has observed increases in fertility in infected women, in a similar vein to good diet and exercise, but with all of the pathological negatives and discomforts the disease carries with it, varying from host to host and again with diet.[18]
Distribution
[edit]Ascaris lumbricoides is primarily distributed in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, particularly in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene practices. It is most prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia (including countries like India, Bangladesh, and Indonesia), and parts of Latin America, where inadequate sanitation infrastructure and the use of human faeces as fertilizer contribute to its spread.[19]
Prevention
[edit]Preventing any fecal-borne disease requires educated hygienic habits/culture and effective fecal treatment systems. This is particularly important with A. lumbricoides because its eggs are one of the most difficult pathogens to kill (second only to prions), and the eggs commonly survive 1–3 years. A. lumbricoides lives in the intestine where it lays eggs. Infection occurs when the eggs, too small to be seen by the unaided eye, are eaten. The eggs may get onto vegetables when improperly processed human feces of infected people are used as fertilizer for food crops. Infection may occur when food is handled without removing or killing the eggs on the hands, clothes, hair, raw vegetables/fruit, or cooked food that is (re)infected by handlers, containers, etc. Bleach does not readily kill A. lumbricoides eggs, but it will remove their sticky film, to allow the eggs to be rinsed away. A. lumbricoides eggs can be reduced by hot composting methods, but to completely kill them may require rubbing alcohol, iodine, specialized chemicals, cooking heat, or "unusually" hot composting (for example, over 50 °C (122 °F) for 24 hours).[20]
Treatment
[edit]Control of roundworm infections is based on treatment with medication, improved sanitation and health education.[21] This usually takes around three days.[22]
History
[edit]Giant intestinal roundworms have been known since antiquity. In 1758 Linnaeus named them Ascaris lumbricoides. For many centuries, they were thought to arise by spontaneous generation. In 1855, Ascaris eggs were found in human faeces by Henry Ransom in England then this was described in the literature two years later by Casimir-Joseph Davaine in France.[23] Attempts to infect animals by feeding them eggs were unsuccessful. In 1886, Salvatore Calandruccio in Italy successfully infected a boy to whom he had given 150 eggs. Battista Grassi published this information without giving any acknowledgement to Calandruccio.[24] Development was thought to occur directly within the bowel lumen but in Francis Stewart in Hong Kong in 1916 fed eggs to rats, then later mice, and found infective larvae in the faeces and in the lungs but no mature worms. In 1918, Sadao Yoshida ingested larvae recovered from the trachea of a guinea pig, then found eggs in his own stools 76 days later. In 1922, Shimesu Koino ingested 2,000 Ascaris lumbricoides eggs, found larvae in his sputum a few days later, then after 50 days took an anthelmintic and recovered 667 immature Ascaris lumbricoides, thus confirming the life cycle.[25]
References
[edit]- ^ "eMedicine - Ascaris Lumbricoides: Article by Aaron Laskey". Archived from the original on 27 January 2008. Retrieved 3 February 2008.
- ^ a b "Parasites - Ascariasis". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 13 June 2023. Retrieved 14 February 2024.
- ^ "Ascariasis, Epidemiology & Risk Factors". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 3 March 2016.
- ^ Leles, Daniela; Gardner, Scott L.; Reinhard, Karl; Iñiguez, Alena; Araujo, Adauto (20 February 2012). "Are Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum a single species?". Parasites & Vectors. 5: 42. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-5-42. ISSN 1756-3305. PMC 3293767. PMID 22348306.
- ^ a b Parasites - Ascariasis. (14 February 2018). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/ascariasis/biology.html
- ^ a b Murray, Patrick R.; Rosenthal, Ken S.; Pfaller, Michael A. Medical Microbiology, Fifth Edition. United States: Elsevier Mosby, 2005[page needed]
- ^ a b c d e Read, A. F.; Sharping, A. (1995). "The evolution of tissue migration by parasitic nematode larvae". Parasitology. 111 (3): 359–71. doi:10.1017/S0031182000081919. PMID 7567104. S2CID 30723471.
- ^ Piper R (2007). Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals, Greenwood Press.[page needed]
- ^ a b Roberts, Larry S.; Janovy, John Jr. Foundations of Parasitology, Eighth Edition. United States: McGraw-Hill, 2009[page needed]
- ^ DoldC; HollandCV (2011). "Ascaris and ascariasis". Microbes and Infection. 13 (7): 632–637. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2010.09.012. hdl:2262/53278. PMID 20934531.
- ^ Tietze, PE; Tietze, PH (1991). "The roundworm, Ascaris lumbricoides". Prim Care. 18 (1): 25–41. doi:10.1016/S0095-4543(21)00914-3. PMID 2011640.
- ^ Dridelle R (2010). Parasites. Tales of Humanity's Mostly Unwelcome Guests. Univ. of California, 2010. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-520-25938-6.
- ^ "DPDx - Ascariasis". Archived from the original on 24 February 2008. Retrieved 3 February 2008.
- ^ Dongjian, Yang; Ya, Yang; Yingjian, Wang; Yu, Yang; Shurong, Dong; Yue, Chen; Qingwu, Jian; Yibiao, Zhou (22 August 2018). "Prevalence and Risk Factors of Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura and Cryptosporidium Infections in Elementary School Children in Southwestern China: A School-Based Cross-Sectional Study". Int J Environ Res Public Health. 15 (9): 1809. doi:10.3390/ijerph15091809. PMC 6165538. PMID 30135364.
- ^ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: Ascariasis
- ^ "INTRODUCTION — Ascaris lumbricoides, an intestinal roundworm, is one of the most common helminthic human infections worldwide". Archived from the original on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 7 May 2012.
- ^ Löffler, W (1956). "Transient Lung Infiltrations with Blood Eosinophilia". International Archives of Allergy and Applied Immunology. 8 (1–2): 54–9. doi:10.1159/000228268. PMID 13331628.
- ^ Blackwell, A. D.; Tamayo, M. A.; Beheim, B.; Trumble, B. C.; Stieglitz, J.; Hooper, P. L.; Martin, M.; Kaplan, H.; Gurven, M. (2015). "Helminth infection, fecundity, and age of first pregnancy in women". Science. 350 (6263): 970–2. doi:10.1126/science.aac7902. PMC 5953513. PMID 26586763.
- ^ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10696405/
- ^ Jenkins, Joseph (1999). "Worms and Disease; Roundworms". The Humanure Handbook - A Guide to Composting Human Manure (2nd ed.). Joseph Jenkins, Incorporated. ISBN 978-0-9644258-3-5.
- ^ "Roundworms: Symptoms and Treatment". 10 February 2023.
- ^ "Roundworms: Parasitic Infection, Pinworm Symptoms, Treatment".
- ^ Grove, David I (1986). "Who discovered that intestinal worm infections could be diagnosed by finding eggs in the faeces?". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 79 (11): 670–673. doi:10.1177/014107688607901118. PMC 1290536. PMID 3540299.
- ^ Grove, David I (2014). Tapeworms, lice and prions: a compendium of unpleasant infections. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 1–602. ISBN 978-0-19-964102-4.
- ^ Grove, David I (1990). A history of human helminthology. Wallingford: CAB International. pp. 1–848. ISBN 0-85198-689-7.
